Introduction
Project
A temporary endeavor that has a specific and unique goal, and usually a budget.
Project management
- What problem are you solving?
- How are you going to solve this?
- Solution
- Requirements
- Deliverables
- Scope
- Solution
- What's your plan?
- Plan
- Work: how long
- Resources
- Schedule
- Process: communication, manage changes
- Plan
- How will you know when you're done?
- Success Criteria
- Quantifiable, measurable results that show that the project is complete
- Success Criteria
- How well did the project go?
Project Management Skills
- Technical
- Business expertise
- Problem-solving
- Interpersonal
- Leadership
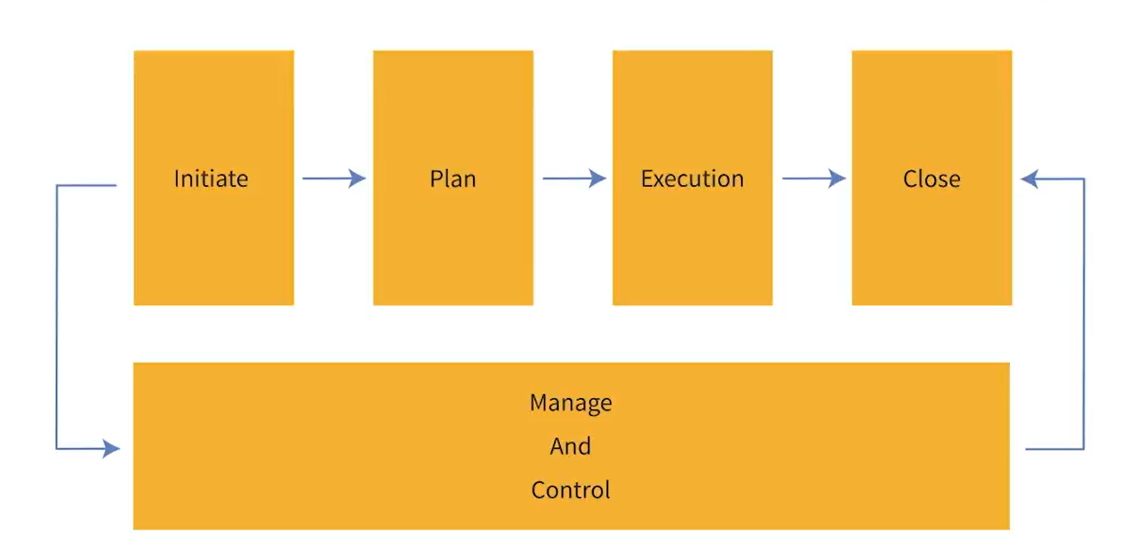
Waterfall Project Management
Traditional project management lifecycle
- Initiating
- Define your project
- Assess scope
- Determine resources needed
- Identify stakeholders
- Ask for approval
- Planning
- What are we going to do?
- How are we going to do it?
- How will we know when it's done?
- Monitoring and Controlling
- Check progress of project
- Compare to what was planned
- Occurs throughout most of the project lifecycle
- Closing Process
- Get client to accept project is complete
- Document project performance
- Gather lessons learned
- Close contracts
- Help resources move to next assignment
Traditional Approach(Waterfall)
Works well when goals are clearly defined.
- Simplicity
- Low risk
- Familiar technology
- Experienced resources
Agile project management
Agile Approach
- Sprints deliver product features at regular intervals
- Value delivered sooner
- More customer involvement
- Small independent teams
Envision
- define the product vision
Speculate(a type of planning)
- Create, revise, and prioritize your feature list
Explore
- Build and deliver the features for the sprint
Adapt
- Review results and change as needed
- Close
- Record lessons learned
Organizational structure
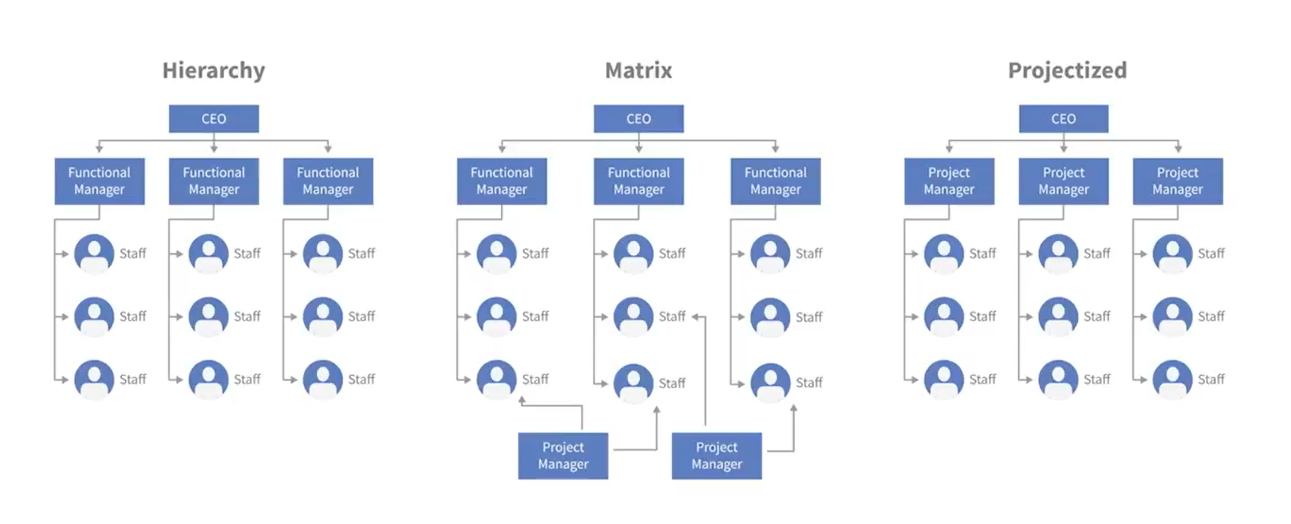
Hierarchy
- PM has almost no authority
- Functional manager in charge of budget
- Resources do not report to PM
- PM has divided responsibilities
Matrix
- PM has some authority
- Resources report to two managers
- PM and staff work full time in a strong matrix
Projectized
- PM has almost complete authority
- Resources are dedicated to project
- PM and admin staff work full time
Document
Ch01-Organization Solution.pdf
Project Management Foundations, with Bonnie Biafore
An Example of Identifying Organizational Structure The following are characteristics of a company I used to work for:
- People report to functional managers. Project managers provide input on employee performance.
- The business unit director oversees budgets for projects within the unit.
- Project managers work predominantly on projects, but also perform other work.
- Project managers have some authority to make decisions. Authority increases after they have delivered successful projects.
This organization is a functional hierarchy with a couple of glimmers of a weak matrix.
Project managers have very little authority. They provide feedback on resource performance to functional managers but don't have authority over resources in other ways. Project managers are given some authority to make project decisions after they have proven themselves. Project managers aren't dedicated to project work.
Organizational Culture
Set of factors that guide people's behaviors and decisions within an organization.
Shaping Culture
- Mission statement
- Leadership
- Work environment
Navigating Culture
- Know the boundaries
- Respect change management
- Respect local culture
Project Management Software
Scheduling Software
- Microsoft Project(weak agile)
- Oracle Primavera(weak agile)
- LiquidPlanner
- Jira(weak waterfall)
- Smartsheet
- Wrike
- Asana
Word Processing
- Microsoft Word
- Google Docs
Spreadsheet
- Microsoft Excel
- Google Sheets
Presentation
- Microsoft PowerPoint
- Keynote
- Prezi
Collaboration
- Basecamp
- Asana
- Microsoft SharePoint
Enterprise
- Complex projects
- Resource assignments
- Tracking
- Document libraries
Considerations
- Culture
- Software budget
- Number of projects
- Complexity
Chapter 1 Challenge
Ch01-Challenge Background.pdf
Project Management Foundations- with Bonnie Biafore
Chapter 1 Challenge
Brisland Hospital Organizational Culture In summary: "Autocratic with a Touch of Compassion"
The culture of Brisland Hospital is autocratic. Doctors provide direct guidance to nurses and other support staff. Decision-making is very hierarchical: what the senior managers decide is typically what will occur. However, the doctors are outspoken and will push back against decisions they believe will degrade patient care or diminish their authority with patient care or staff management.
The expectation of all hospital staff is that patient care comes first. Tat expectation can lead to financial pressures when the care provided will not be fully paid for by insurance companies. Pursuing patients for past due amounts is time-intensive and emotionally trying for the hospital's administrative staff.
Senior managers exhibit a "silo mentality." They make decisions in the best interest of their responsibilities within the hospital, rarely conferring with their senior management peers. Dr. Olsen, the COO, will intervene and force the senior leaders to work together only when she believes significant benefits may result, or significant issues will arise from a lack of communication.
In general, hospital staff are cared for reasonably well. They are overworked, due to a deep-seated expectation that compassion be shown to patients. The hospital has a reputation for being friendly with patients and their families. Staff see the more demanding side of the hospital culture. However, in times of need or strife, hospital management will show significant compassion for their staff. Some say that compassions needs to be shown before staff get to the breaking point, but acknowledge it is provided abundantly when significant needs arise.
Brisland Hospital Organizational Structure
Dr. Carla Olsen, as the project sponsor and the hospital's Chief Operating Officer(CEO), has significant authority and influence.
Dr. Olsen is very busy. She manages Physician and Patient Services. Hospital facilities are managed by Nicholas Anderson, the VP of General Services. The purchase and management of the hospital's technical equipment and staffing are managed by Marid Diaz, the Financial Controller. The VP and Financial Controller are Dr. Olsen's management peers (see the organization chart for Brisland Hospital).
第 1 章挑战
布里斯兰医院组织文化 总结:“专制与同情”
布里斯兰医院的文化是专制的。 医生为护士和其他支持人员提供直接指导。 决策是非常分层的:高级管理人员的决定通常就是将要发生的事情。 然而,医生们是直言不讳的,他们认为会降低患者护理或削弱他们在患者护理或员工管理方面的权威的决定会予以抵制。
所有医院工作人员的期望是患者护理至上。 当保险公司无法全额支付所提供的护理费用时,这种期望可能会导致财务压力。 对于医院的管理人员来说,追查患者逾期未付的款项是一项耗时且费力的工作。
高级管理人员表现出“筒仓心态”。 他们根据医院职责的最佳利益做出决策,很少与高级管理人员协商。 首席运营官奥尔森博士只有在她认为可能会带来重大利益,或者由于缺乏沟通而出现重大问题时,才会进行干预并迫使高层领导共同努力。
总的来说,医院工作人员得到了相当好的照顾。 由于对病人表现出同情心的根深蒂固的期望,他们工作过度。 该医院以对患者及其家属友好而享有盛誉。 工作人员看到了医院文化中要求更高的一面。 然而,在需要或冲突的时候,医院管理层会对员工表现出极大的同情心。 有人说,在员工达到极限之前,需要表现出同情心,但也承认,当出现重大需求时,人们会充分提供同情心。
布里斯兰医院组织结构
Carla Olsen博士作为项目发起人和医院的首席运营官(CEO),拥有显着的权威和影响力。
奥尔森医生很忙。 她负责管理医生和患者服务。 医院设施由总务副总裁尼古拉斯·安德森 (Nicholas Anderson) 管理。 医院技术设备和人员配置的采购和管理由财务总监 Marid Diaz 负责。 副总裁和财务总监是 Olsen 博士的管理同事(请参阅布里斯兰医院的组织结构图)。
Brisland Hospital Organization Chart
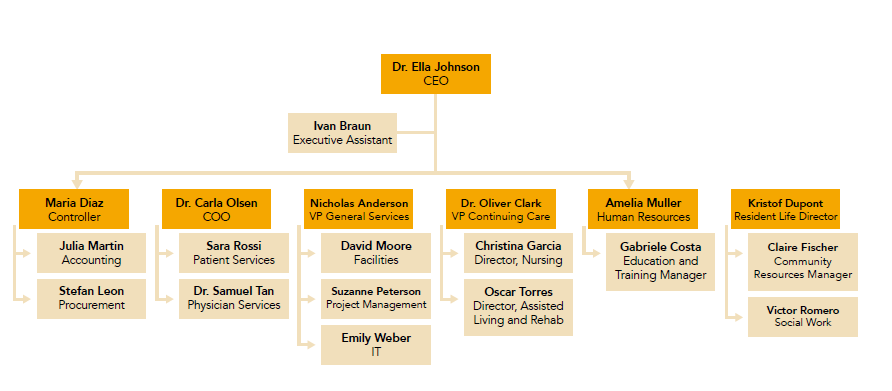
- As the project manager, what advantages could you have with hospital COO being the project sponsor?
- How could Dr. Olsen's busy schedule affect your ability to manage the project?
- What advantages will Dr. Olsen's responsibility as manager of Physician and Patient Services provide to your project?
Sample solution
Project Management Foundations with Bonnie Biafore
Chapter 1 Solution
While we can never be completely certain about what may happen on a project, the culture and organizational structure for the hospital will have an effect, so it is important to consider the challenge questions. Here are my answers to these questions, which you can compare to your own thoughts:
What advantages might you experience due to Dr. Olsen’s position as the hospital COO?
As the COO, Dr. Olsen will have significant influence and exposure to a large percentage of activity in the hospital. She will be very knowledgeable and understand how the hospital’s culture and organization will affect your project. That information will be critical for you to successfully guide the project.
What advantages and disadvantages will Dr. Olsen’s busyness provide relative to your ability to man-age the project?
Dr. Olsen’s time for assisting you will be limited. Her allocation of time to your project will probably be influenced by the hospital’s culture for supporting projects. As a project manager, you will have to use Dr. Olsen’s time wisely and efficiently. You may also have to be flexible when working with her to accommodate her schedule and management priorities.
What advantages will Dr. Olsen’s responsibility as manager of Physician and Patient Services provide to your project? What potential disadvantages will the management responsibilities of others (the purchase and management of the hospital’s technical equipment and staffing) have to your project?
Because your project involves scheduling hospital facilities for the benefit of patients and physicians, Dr. Olsen will have direct influence over significant aspects of your project, which is a valuable organizational advantage. However, with the new cancer ward construction and the amount and availability of facilities is managed by others, Dr. Olsen’s influence will be indirect. You and Dr. Olsen will have to work closely with her management peers. You will need to understand the organizational influence and the management culture that exists among the hospital’s management team. At best, it is a disadvantage because it will involve more time and effort working with other significant stakeholders. At worst, if Dr. Olsen and her peers don’t have good working relationships or they have differing opinions, you may require significant negotiation and finesse to manage the project. The culture of how decisions are made and how disagreements are resolved will influence the management of this project.
Quiz
- Your project seems to be going off track, so you take action to resolve the problem. In which project management phase are you working?
- Planning
- Executing
- Monitoring and Controlling
- This phase checks on the status of the project and compares it to what was planned.
- Closing
- The boss has asked you to research project management tools that will help with building and planning tasks on a timeline. Which type of tool would you most likely consider?
- a scheduling program
- Project managers typically use this tool to build and manage a project schedule.
- a presentation program
- a collaboration program
- a spreadsheet program
- a scheduling program
- During which waterfall phase does the project manager bring the full team on board and orient them to the project and expectations?
- monitoring and controlling
- executing
- At the beginning of the executing phase, you kick off the project, get resources on board, and explain the rules for the project.
- planning
- initiating
- Your organization runs numerous projects and wants to choose the most appropriate resources for each project team. Which of the following is the best tool for identifying project resources?
- scheduling software
- enterprise project management software
- Enterprise project management software offers tools to find resources with the right skills and availability.
- a collaboration tool
- a spreadsheet program
- You are hiring a new project manager to take over a project with several teams that often disagree on what they are supposed to do. Which competency would you feel is most important in a candidate for this situation?
- business expertise
- strong leadership skills
- This skill is needed to help guide and inspire the team to do the right things and work together.
- technical skills
- problem-solving skills
- Which organizational factor is most important when you need to make a difficult decision?
- the organization's leadership
- the organization's mission
- When a project supports the organization's mission, the project will likely get more support and resources, so the mission helps determine the best thing to do.
- the organization's work environment
- the organization's authority
- Which of the following skills is not crucial for a project manager to possess?
- business expertise
- leadership
- accounting
- Although project managers do need to understand aspects of finance, accounting skills can be provided by others.
- interpersonal skills
- Camille wants to use the Agile approach on the project she will be managing. What significant benefit does the agile methodology provide?
- The project goals don't change over the course of the project.
- The customer receives value from the project sooner.
- One of the key benefits to an agile methodology is that the customer receives value sooner, because partial solutions are delivered on a regular schedule.
- The solution is defined at the beginning of the project.
- The project team is more experienced.
- A project that you manage is behind schedule. You have identified an approach that would get the project back on track, but it would require you to break one of your organization's policies. What is the best course of action?
- Inform the management team that there is no way to meet the schedule deadline.
- Determine if the rule is one that can be broken and come up with an alternative plan of action if your approach doesn't work.
- Some rules can't be broken without severe consequences. If you determine that the rule can be broken, you can deliver earlier with minor consequences. You must have a plan for what you will do if you break the rule and don't deliver earlier.
- Move forward with your plan. You can ask for forgiveness later.
- Continue the project without implementing the approach you identified and look for other places to get the project back on track.
- Rosanne's boss asks her to manage a project. Which question requires understanding of objectives, requirements, deliverables, and success criteria to answer?
- How will you know when you are done?
- This question requires understanding of deliverables and success criteria, whereas the other questions do not require that information.
- What problem are you solving?
- What is your plan?
- How are you going to manage the project?
- How will you know when you are done?
- James is managing a project in which he has some authority to make decisions. In which type of organizational structure is James most likely managing this project?
- none of these
- a matrix organization
- This organizational structure can be weak or strong, but does allow the project manager to have some authority to make decisions.
- a pure functional hierarchy organization
- a projectized organization
- What are the components that differentiate a project from operational work?
- a unique goal and dedicated resources
- specific requirements, start and finish dates, and management approval
- a unique goal, a temporary endeavor, and usually a budget
- The definition of a project is "a temporary endeavor that has a unique goal and usually a budget."
- a unique goal and requirements for that goal
- Ravi took on a system implementation project that he estimated would take six months to complete, but the work keeps continuing. What is the likely cause?
Management didn't stipulate specific beginning and end dates.- A project is a temporary endeavor that has a specific time frame for completion. In this case, Ravi had an end date in mind, so the lack of a management end date isn't the problem.
The project has access to resources to do more work.- Resources are usually a constraint on a project. Available resources could do more work, but that is not the likely cause of the work failing to end.
- The project has budget remaining.
- The project is not clearly defined.
- When the work on a project keeps going, it is a sign the project is not well defined.
