Chapter 2: Intelligent Autonomous Vehicle
OBJECTIVES
- Overview
- History of Intelligent and Autonomous Vehicle
- Classification of Autonomous Vehicle Based on Driving Levels
- State of the Art of Intelligent and Autonomous Vehicle Technologies + Battle for Adoption
- Market Demand of Automotive Cyber Security
OVERVIEW
- This chapter provides an overview of the developments in intelligent and autonomous vehicle (IAV) that accompany in-vehicle and inter-vehicle connectivity.
- This chapter gives detailed information regarding the evolution of intelligent and autonomous vehicles, its classification based on vehicle driving levels, associations between connectivity and autonomy for vehicle performance and the state-of-the-art applications.
- The intelligent and autonomous vehicle technologies can be categorized into autonomous vehicles also known as self-driving vehicles and Cooperative Intelligent Transport Systems (C- ITS), which is also known as connected vehicle.
- The connected vehicle technologies are based on vehicular ad hoc networks also known as VANETs for transmitting beacon messages, basic safety messages, and infotainment messages. Hence, IAV is the next-generation self-driving vehicle equipped with different types of advanced sensors, actuators, controllers incorporated with intelligence and cooperative driving capability to guarantee autonomy, safety, protection, ease, and energy-efficient.
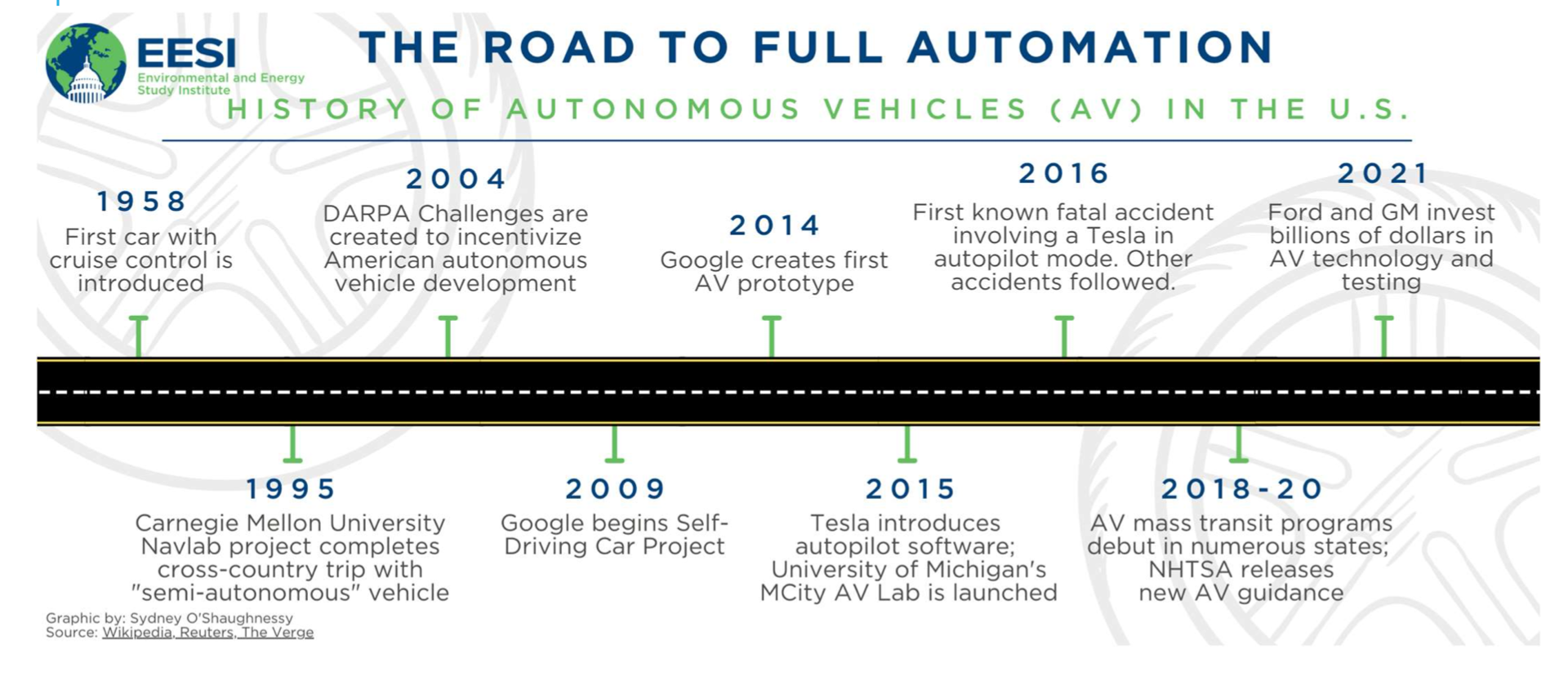
HISTORY OF INTELLIGENT AND AUTONOMOUS VEHICLE
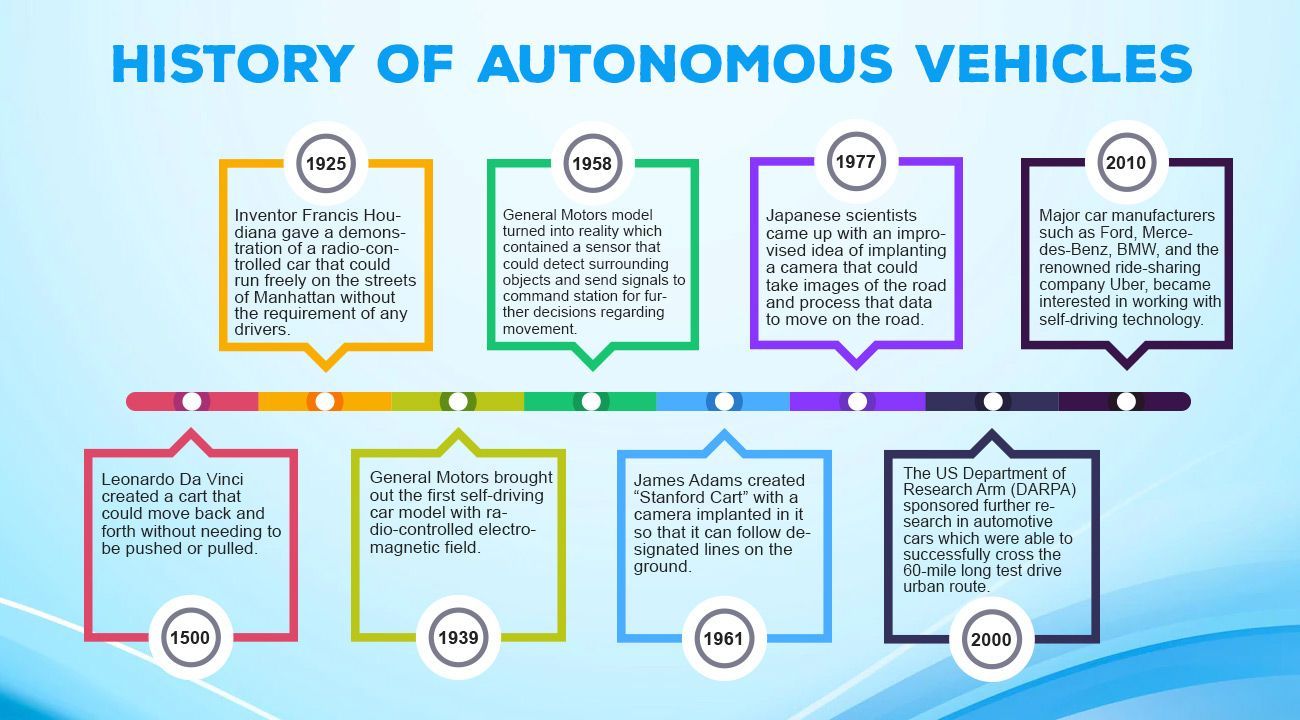
Source: https://techinspection.net/development-history-and-future-of-self-driving-autonomous-cars/#google_vignette
CLASSIFICATION OF AUTONOMOUS VEHICLE BASED ON DRIVING LEVELS
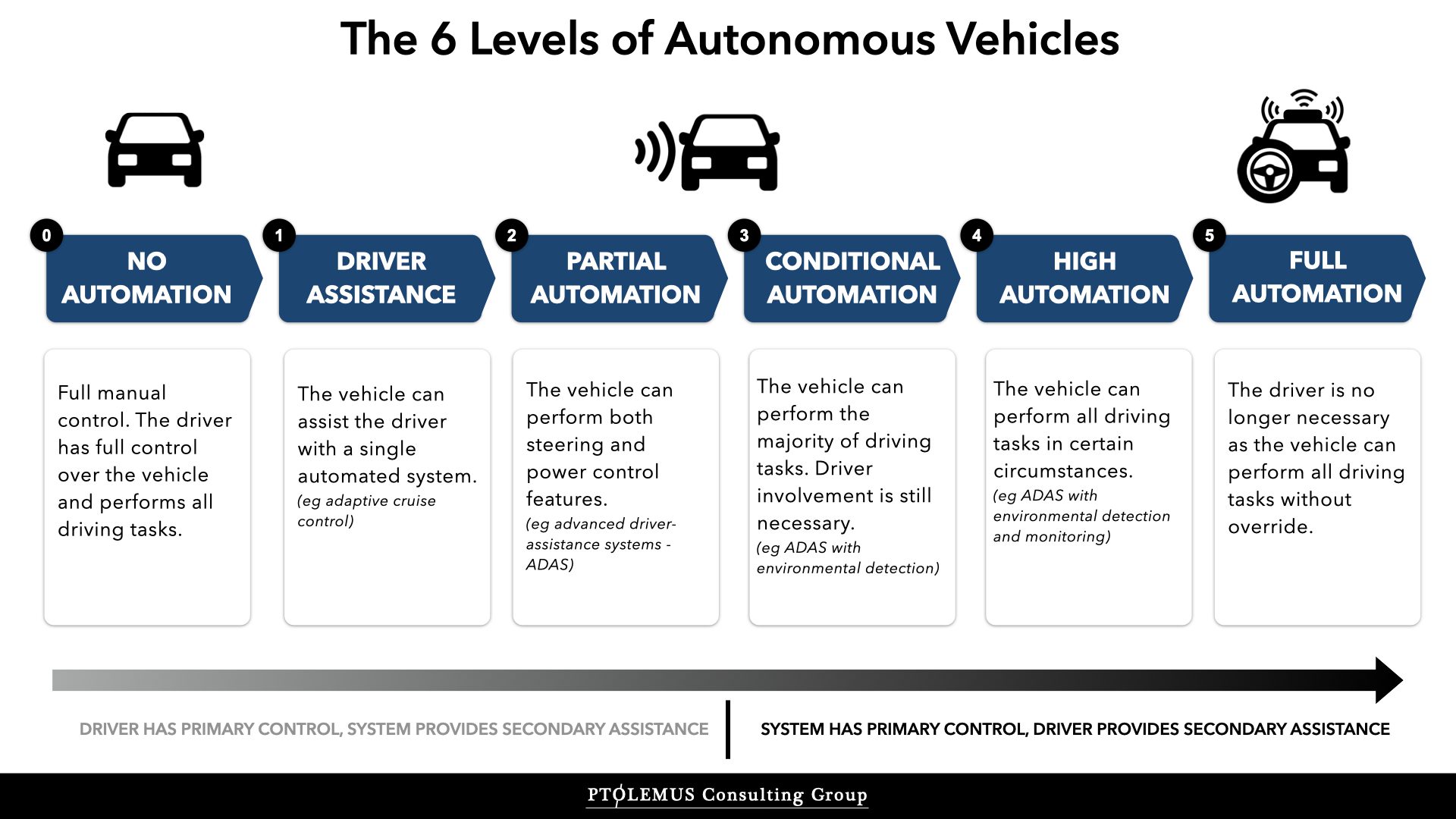
Source: https://www.ptolemus.com/wp-content/uploads/The-6-Levels-of-Autonomous-Vehicles_PTOLEMUS.001.jpeg
STATE OF THE ART OF INTELLIGENT AND AUTONOMOUS VEHICLE TECHNOLOGIES: IN-VEHICLE COMMUNICATION
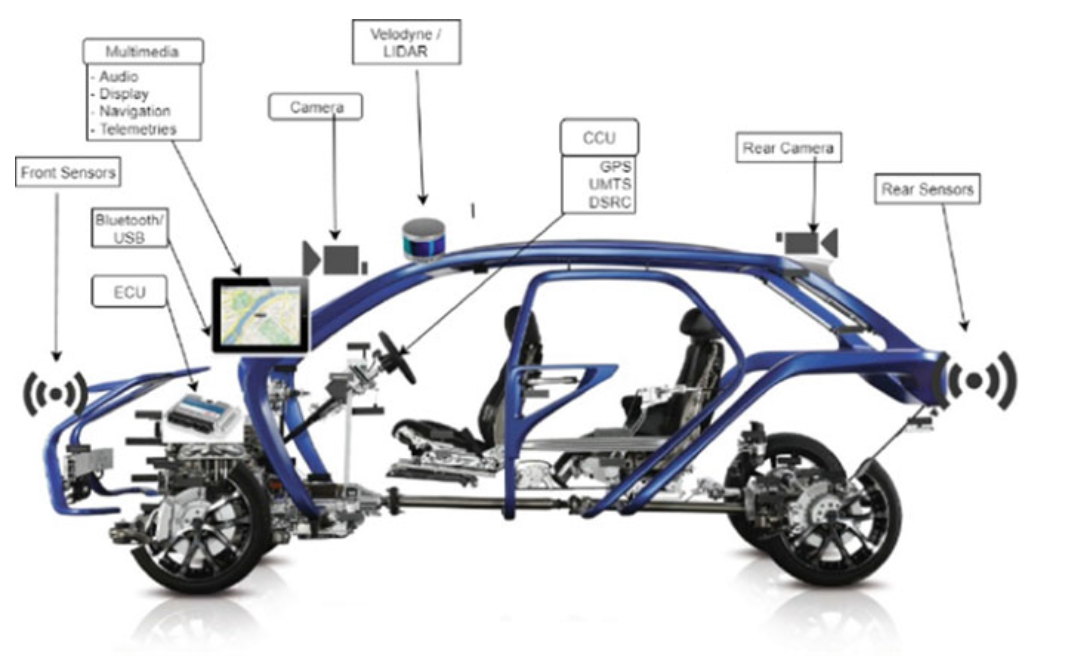
Fig. 2.3 Autonomous vehicle functional components with sensor fusion
STATE OF THE ART OF INTELLIGENT AND AUTONOMOUS VEHICLE TECHNOLOGIES: IN-VEHICLE NETWORKING TYPES
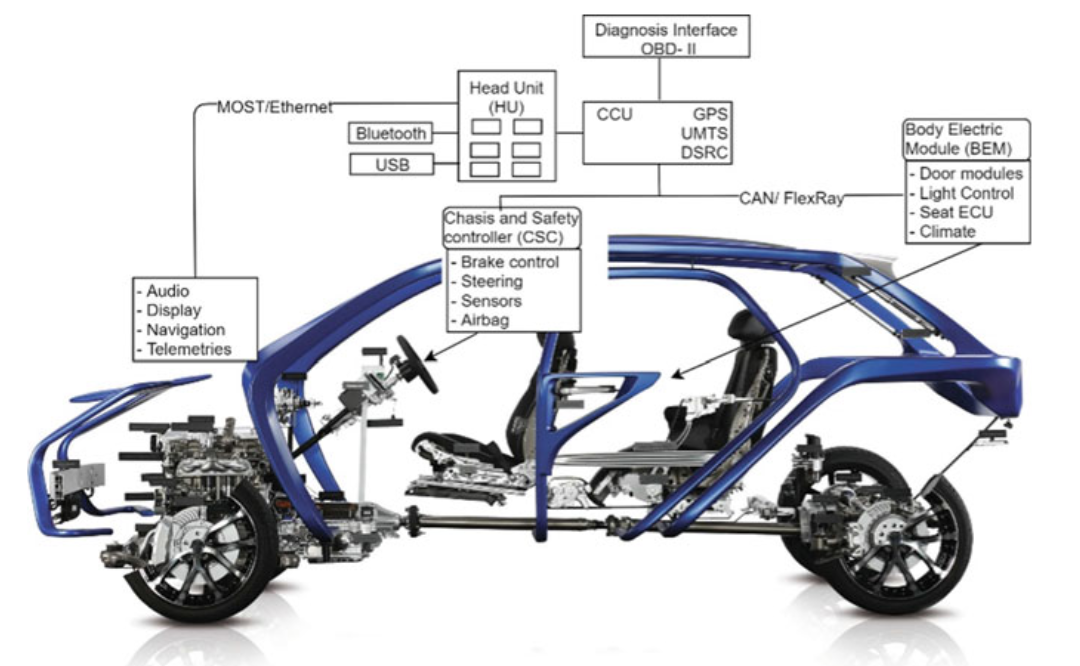
Fig. 2.4 In-vehicle networking system
In-Vehicle Networking Types
- FlexRay
- Controller Area Network (CAN)
- Local Interconnect Network (LIN)
- Automotive Ethernet (AE)
- Media Oriented Serial Transport (MOST)
CONNECTED VEHICLE TECHNOLOGY
- In Cooperative Intelligent Transportation System (C-ITS), also known as connected vehicle technology largely, depends on VANET for transmitting basic safety message, non-safety messages like multimedia messages along with infotainment messages.
- Recently, connected vehicles have gained a lot of attention from industry and academia that could potentially help the safe driving, and traffic situation such as congestion, accident, and road construction.
- The advancement of connectivity in vehicles includes different types of communication technologies for autonomous vehicles.
- The communication between the vehicles and its surroundings such as neighbor vehicles, pedestrian, RSU is based on inter-vehicle communication.
INTER-VEHICLE COMMUNICATION
- In inter-vehicle communication, the vehicle can communicate with other vehicles as well as with infrastructure and the cloud using wireless communication.
- The inter-vehicle communication depends on VANET technology.
- VANET uses diverse kinds of communication protocols based on the type of communication and type of infrastructure.
- In VANET, the Wireless Access in Vehicular Environments (WAVE) protocol provides the basic radio standard for dedicated short-range communication (DSRC) operating in the 5.9 GHz frequency band, which is based on the IEEE 802.11p standard.
- In addition to this, emerging cellular technologies such as LTE and 5G technology can be used for V2X communication in VANET.
- Vehicular communications can be achieved in the infrastructure domain for vehicle-to- infrastructure (V2I) communications to connect to roadside units (RSUs) or in the ad hoc domain for vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communications or vehicle-to everything (V2X) communications.
BATTLE FOR ADOPTION
- The FCC has introduced the DSRC standard more than two decades in the field of intelligent transportation service to provide safety and efficacy of the vehicles on the road.
- In the USA, the federal government proposed a mandate to implement V2V in new vehicles based on DSRC.
- Two groups of global automakers and research institutes work toward using wireless communication in autonomous vehicles.
- One group is attracted toward using DSRC technology in autonomous vehicles while the other groups support the use of C-V2X technology due to its potential and evolution toward 5G.
- They switched their focus to C-V2X platform and involved in chip making, testing, and demonstration.
- Since cellular technology is not mature in vehicular communication field compared to DSRC, it might take some time to be widely deployed, as it has not been extensively tested.
- It is operated in licensed band without dedicated and specific MHz band.
- The 5GAA and other research institutes like Qualcomm and Huawei back up this technology and advocate for C-V2X adoption because of its advantages in vehicular communication.
MARKET DEMAND OF AUTOMOTIVE CYBER SECURITY
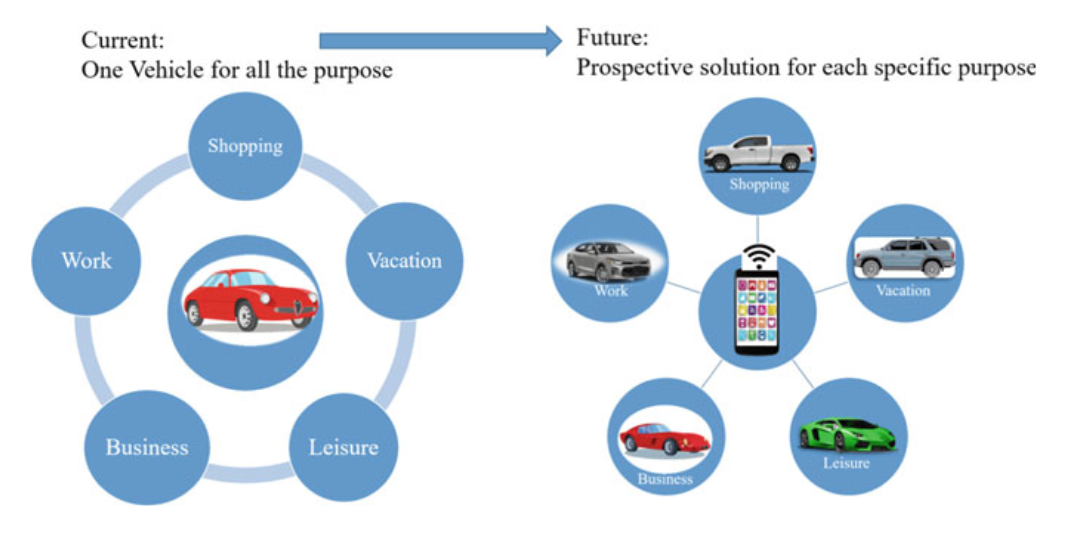
Fig. 2.10 Prospective mobility solution for performing specific purposes
- Traditionally, the automotive industry has been conservative in adopting features offered by consumer electronics. However, the connected vehicle is finally becoming a reality, and it will likely redefine the entire automotive industry.
- Vehicle manufacturers must find ways to deliver the advanced features their customers demand, into their “smartphones- on-wheels.”
- They will also need to embrace security solutions that are widely used in smartphones and IT infrastructures, but that are relatively new to the automotive world.
- Examples of such technologies are firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, virtualization technologies, and secure firmware updates.
