An Overview of Blockchain Technology: Applications, Challenges and Future Trends
Wenzheng Li,Mingsheng He
Faculty of Information Technology Beijing University of Technology Beijing, China liwww@bjut.edu.cn
Abstract:
Starting from the basic concept of blockchain technology, the paper introduces the architecture of blockchain technology and the typical application of blockchain technology, and finally summarizes the challenges faced by blockchain technology, so as to provide some reference for the technological path innovation and data value reconstruction of deep integration of blockchain technology and various fields.
Keywords - Blockchain; Decentralization; Consensus Mechanism; Smart Contract
I. Introduction
Blockchain Technology (BT) is a new decentralized infrastructure and distributed computing paradigm, which uses encrypted chained data blocks to verify and store data, uses distributed node consensus algorithms to generate and update data, and uses smart contracts to program and operate data. Its outstanding feature is that it doesn't rely on third-party trusted organizations to realize value communication between nodes without a trust relationship.
Blockchain is a novel type of distributed infrastructure and computing paradigm that integrates technologies including distributed data storage, peer-to-peer (P2P) transmission, consensus algorithms, and cryptography [1]. It uses blockchain data structures to store and verify data, uses distributed consensus algorithms to generate and update data, uses cryptography technologies to ensure the security of data transmission and access, and uses smart contracts composed of automated script codes to program and operate data [2]. Through the integration of multiple technologies, the cluster jointly maintains the security and operation of the blockchain network and builds trust with machines.
Blockchain has four major supporting technologies: distributed database, consensus algorithm, secure cryptographic protocol, and smart contract. Based on the underlying key technologies of the blockchain, it has the following characteristics [3]:
- Decentralization: There is no centralized hardware or management organization in the blockchain network. The rights and obligations of all nodes are equal, and the data in the system is maintained together. The suspension of any node does not affect the overall operation of the system.
- De-trusting: The system generates trust through cryptography, verification, and other methods, and all nodes can conduct trusted transactions without third-party guarantees.
- Tamper Proof: Once the data is written into the blockchain, it cannot be changed or undone.
- Openness and Transparency: In a very short period, the block will be copied to all nodes in the cluster, realizing data synchronization across the network, and each node can trace back all past transaction information.
- Security: Every node in the system has the latest and complete copy of the data. The attack of malicious nodes is difficult to work because the system considers the same data record that appears most often to be true.
On October 30, 2008, a person with the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto published a report titled "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System" [4] on the cryptography forum, which fully explained the principles of Bitcoin and the blockchain technology. International scholars' research on the blockchain started since then. Bitcoin is a P2P electronic cash system. Anyone can join the Bitcoin system at any time and transfer Bitcoin to each other through anonymous addresses. The transactions generated in a certain period will be sorted into a block, and the newly generated block will be linked to the back of the previous block, thus forming a blockchain. This is where the concept of blockchain comes from [5]. The blockchain in the Bitcoin system is also called the ledger, which records all transaction records of Bitcoin since its birth and is distributed on various nodes in the network.
Ethereum is a programmable blockchain platform [6]. On the Ethereum platform, users can not only perform some predefined operations (transactions) but also create their complex operations on it. As a platform, Ethereum can provide services for different applications. In a narrow sense, Ethereum is a virtual machine composed of a series of protocols, which can execute any complex code based on protocol standards. The Ethereum virtual machine (EVM) is Turing-complete. So developers can create their applications on virtual machines using the Solidity language [7].
- Libra is a cryptocurrency project initiated by Facebook [8]. Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies have caused large fluctuations in their currency prices due to deflation mechanisms and other reasons. People hardly use them to make payments, and they become digital assets based on consensus finally [9]. The goal of Libra is to become a stable cryptocurrency [10]. From the perspective of the underlying technology, the Libra blockchain is a consortium blockchain based on the LibraBFT consensus algorithm, which refers to the design of Ethereum in its implementation and will move towards a public blockchain based on Proof of Stake (PoS) [11] in the future. There are three requirements during the consortium blockchain period:
- Scalable: The system can scale to billions of accounts, achieve extremely high transaction throughput and low latency, and have an efficient and high-capacity storage system.
- Reliable: This means it can guarantee the security of funds and financial data.
- Flexible: This means it is enough to support the management of the Libra ecosystem and future innovations in the field of financial services.
In particular, Libra proposes a complete programming system called Move for digital assets [12]. Compared with existing blockchain programming languages such as Solidity, Move focuses on strengthening the status of digital assets. Using the Move language, developers can define and manage digital assets on the Libra blockchain more flexibly.
Blockchain has gone through several stages of technological evolution [13]. Blockchain technology originated from cryptocurrency and has experienced the 1.0 era represented by cryptocurrency and the 2.0 era represented by smart contracts. It is currently entering the 3.0 era, which is deeply integrated with various industries. It is combined with emerging technologies such as big data and artificial intelligence (AI). In the future, blockchain 3.0 is a variety of blockchain applications deeply embedded in social life based on smart contracts. People can use smart contracts for financial management, entertainment, learning, etc. New types of blockchain technologies such as heterogeneous networks, neural network consensus, and sharing of computing power within and outside the blockchain will appear.
II. BASIC TECHNOLOGY OF BLOCKCHAIN
In a broad sense, blockchain technology is a new distributed infrastructure and computing paradigm, which uses blockchain data structure to verify and store data, uses distributed node consensus algorithm to generate and update data, uses cryptography to ensure the security of data transmission and access, and uses intelligent contract composed of automated script code to program and operate data.
A. Distributed Storage
Although Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) is often considered synonymous with blockchain technology, distributed ledger refers to a database of assets that are jointly governed and shared in a network composed of multiple sites, different geographic locations, or multiple institutions [14]. From the perspective of computer technology, the ledger is a data structure that contains transactions and information. The ledger can record multi-party fund exchange records and item exchange records. In the blockchain system, transactions are organized into blocks, and then the blocks are organized into logical chains. Therefore, the blockchain is a decentralized, growing, and immutable ledger. The ledger can be completely open or open within the alliance.
B. Asymmetric Encryption
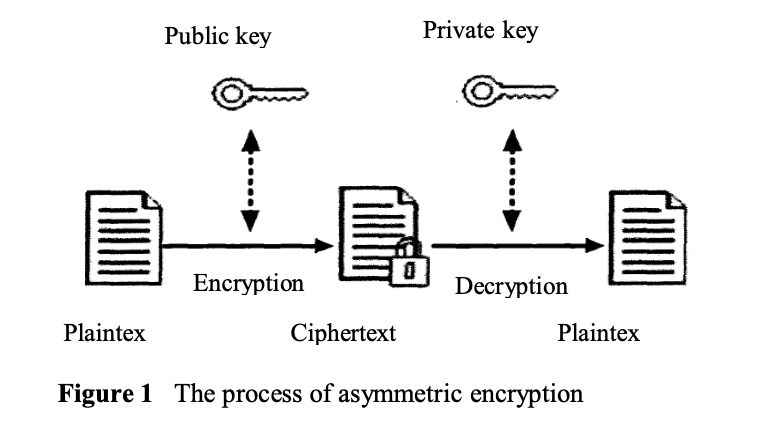
Asymmetric encryption, also known as public-key cryptography, is a key-based security method [15]. There are two keys in asymmetric encryption algorithms: a public key and a private key, and the public key and the private key always appear in pairs. If a public key is used to encrypt certain data, only the private key generated with the public key can be used to decrypt. Conversely, only the public key corresponding to the private key can decrypt data encrypted by the private key. Because the two keys used for encryption and decryption in this algorithm are different, it is called an asymmetric encryption algorithm. Figure 1 shows the process of encryption and decryption. In the blockchain, the signature of a transaction is strictly related to the content of the transaction. If a person uses the same private key to sign different transaction content, the signature will also be different. This is an advantage over manual signing.
C. Merkle Tree
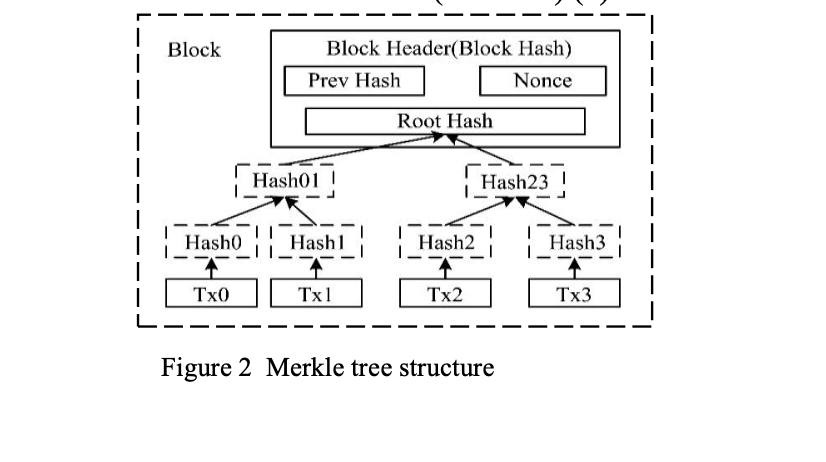
Merkle Tree [16] is a kind of hash binary tree, which can quickly summarize and verify the integrity of large-scale data. In the blockchain, the transactions storage in each block is in the form of the Merkle Tree method. The leaf node of the Merkle Tree in the block is the hash value of each transaction, and then the hash is made from the bottom to the top. Finally, the value of the Merkle Tree root will eventually be stored in the block header. The blockchain uses the characteristics of the Merkle Tree to ensure that every transaction cannot be tampered with.
Assuming that there are 4 transactions in the current block, the above process is described by the formula as follows and shown in Figure 2, where SHA256 is the SHA-256 hash function.
Conclude the nodes in the first layer:
[ H_{12} = \text{SHA256}(H_0 + H_1) ]
[ H_{34} = \text{SHA256}(H_2 + H_3) ]
Conclude the nodes in the second layer:
[ H*{1234} = \text{SHA256}(H*{01} + H_{23}) ]
D. Consensus Algorithm
The disruptive nature of the blockchain is reflected in the fact that it breaks the rule that trust must be endorsed by a third party, and realizes the direct establishment of trust between nodes. The consensus algorithm guarantees the credibility of information in a trustless environment and has been a hot spot in distributed system research in recent years [17]. At the same time, the consensus algorithm is the key technology of the blockchain, which directly affects the efficiency, scalability, and resource consumption of the blockchain system. At present, researchers have completed a lot of work in the consensus field. From the perspective of how to elect a leader node, the existing consensus algorithms can be divided into the following five types [18]:
Proof consensus: The miner nodes must prove that they have a certain ability in each round of consensus. The proof method is usually to competitively complete a task that is difficult to solve but easy to verify. The miner node that wins the competition will obtain accounting rights, such as Proof of Work (PoW) and PoS.
Election consensus: The miner nodes select the current leader node by voting during each round of consensus. The miner node that first obtains more than half of the votes will get the right to generate a block. Traditional distributed consensus algorithms are mostly such consensus, such as Paxos and Raft.
Random consensus: A miner node is directly determined as the leader node of a round according to a certain random method.
Consortium consensus: The miner nodes first elect a group of representative nodes based on a certain method, and then the representative nodes obtain the accounting rights in turn or by election.
Mixed consensus: The miner nodes adopt a mixture of multiple consensus algorithms to select the leader node.
The consensus algorithm mainly solves two basic problems: one is which node generates the block, and the other is how to synchronize the block[13]. The block chain, each node independently maintains the same data. In order to avoid data confusion, a fair election mechanism and a reasonable incentive mechanism must be designed. After the elected node writes data, other nodes must synchronize the data accurately in time, and verify the legality of the new data to avoid forgery and illegal writing of data. Different consensus algorithms have different election mechanisms. During a round of consensus of the blockchain, the elected nodes first package transactions to construct the block and broadcast it. Secondly, all nodes in the blockchain network verify the legality of the received block according to the consensus algorithm. If the block is legal, it will be appended to the end of the current blockchain to complete a data update process.
In 2008, Satoshi Nakamoto mentioned the PoW algorithm for the first time in his explanation of the Bitcoin system. Due to its simple principle and stable execution, PoW has become the mainstream underlying consensus algorithm in major cryptocurrency applications. In the Bitcoin system, new transactions are generated all the time, and nodes need to put legal transactions into blocks. The block header contains 6 parts, which are the version number, the hash value of the previous block, the Merkle tree root value, the timestamp, the difficulty target, and the random number. Participants, also called miners, need to look for a random number to make the hash value of the block header less than or equal to the difficulty target. For example, the binary representation of a difficult target consists of 32 zeros, and it takes an average of 232 attempts to solve this problem. The difficulty target will be adjusted every 2016 blocks so that the average rate of block generation will be kept at every 10 minutes. PoW guarantees that the transactions appearing in the system within a period of time can be calculated. However, PoW also has significant shortcomings. The waste of electric power resources caused by its computing power consumption has always been criticized by people, and the 10 minute transaction confirmation time makes it relatively unsuitable for commercial applications where small transactions mostly exist.
In 2014, at the beginning of the Ethereum launch, the team announced that the project's release would be divided into four phases, namely Frontier, Homestead, Metropolis, and Serenity [20]. The consensus algorithm of the first three stages adopts PoW and the fourth stage switches to PoS. In the PoS, the node with the highest stack but not the highest computing power in the system obtains the right to book- keeping, where the stack is reflected on the node's ownership of a specific amount of currency, called coinage. The coinage is calculated by multiplying the coins owned by the miner by the remaining usage time of each coin as shown in formula 4:
Coinage = number of coins*remaining use time of coins (4)
The criteria for judging legal blocks can be expressed as: hash(block_header) =< target * coinage (5)
This means that the more coins you have, the easier it is to get the answer. In this way, PoS solves the problem of wasting computing power in PoW to a certain extent and can shorten the time for reaching consensus. Therefore, many cryptocurrencies after Bitcoin adopt PoS. However, there is still a mining process in PoS, which essentially does not solve the pain point of commercial applications, and it will bring centralized results in extreme cases.
The Libra blockchain uses the LibraBFT consensus algorithm based on HotStuff [21] in the BFT algorithm cluster. According to the Libra white paper, the reasons for improving based on the HotStuff algorithm are as follows:
- the simplification and modularization of the security demonstration;
- easy to reach a consensus;
- the algorithm has good performance in the early experiments. LibraBFT regulates and improves HotStuff through the Pacemaker mechanism. And put forward the algorithm activity analysis including detailed constraint conditions of transaction confirmation. LibraBFT ensures that the blockchain network can still operate normally even when at most 1/3 of the nodes fail. Compared with other election consensus algorithms, LibraBFT has the advantages of low latency and high throughput.
Table I compares the performance of PoW, PoS, and LibraBFT in terms of decentralization, consensus efficiency, the ratio of fault-tolerant and resource consumption.
Table I. Consensus Algorithm Comparison Results
| Evaluation Criteria | Consensus Algorithm | - | - |
|---|---|---|---|
| - | PoW | PoS | LibraBFT |
| Degree of decentralization | high | high | low |
| Consensus efficiency | low | medium | high |
| The ratio of fault-tolerance | 50 | 50 | 33 |
| Resource consumption | high | medium | low |
E. Smart Contract
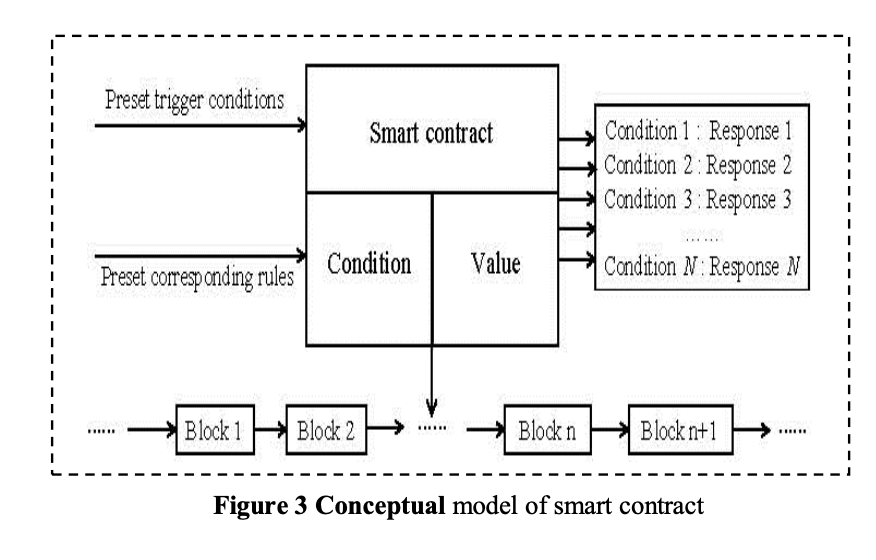
The concept of a smart contract was proposed by Nick Szabo in 1994. He defined a smart contract as a computer program implementation of the terms of the contract, which can ensure the correct performance of the contract without a trusted third party. The conceptual model of the smart contract is shown in Figure 3.
Generally speaking, smart contracts encapsulate several predefined states, conversion rules, trigger conditions, and response operations, etc., which are stored on the blockchain in the form of program code after being signed by all parties [19]. After it is recorded in the distributed ledger of each node, the blockchain can monitor the status of the smart contract in real-time, and activate and execute the contract after checking the external data source to confirm that the specific trigger conditions are met.
III. BLOCKCHAIN TECHNOLOGY ARCHITECTURE
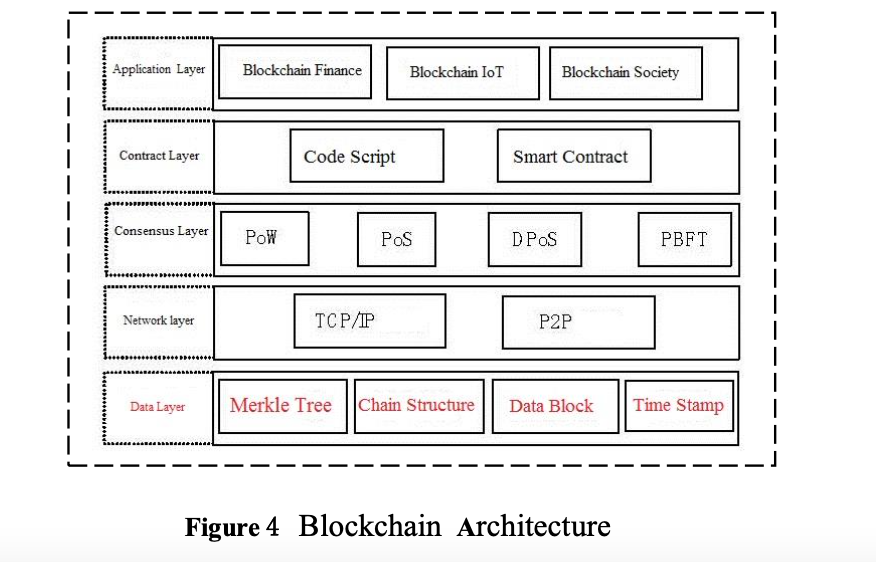
Blockchain, as a combination of various computer technologies, has a hierarchical architecture with different functions but mutual support. Among them, the consensus layer solves the trust problem between unfamiliar nodes; the contract layer gives the blockchain good scalability. At present, all kinds of blockchain platforms adopt the same architecture. It can be divided into data layer, network layer, consensus layer, contract layer, and application layer. There are five levels. Its architecture is shown in Figure 4.
A. Data Layer
Data layer includes data structure, data model and block storage. It is the basic layer of blockchain architecture and a distributed ledger to store transaction or account information. Merkle tree stores intra block information based on transaction data hash, which determines the "tamper proof" feature of blockchain. Data blocks are arranged according to timestamps and connected into a chain structure by hash pointers, which determines the "traceability" characteristics of blockchain.
B. Network Layer
Network layer blockchain network layer is a distributed network without the supervision of the third-party central organization. It realizes the distributed structure based on P2P technology and the point-to-point communication based on TCP/IP communication protocol. Each node plays the role of receiving and forwarding information. The distributed network characteristics determine that each node has all the information of the system, and the normal operation of the system will not be affected if a single node is attacked.
C. Consensus Layer
There is no central node supervision in the blockchain network, and the responsibility of network maintenance needs to be undertaken by multiple parties, which requires a mechanism to ensure that each node can reach a consensus. Once a consensus is reached, the transaction information in the block will be officially put into effect on the chain, and backup will be provided to each node in the network. Consensus mechanism provided by consensus layer determines that blockchain has the characteristics of "self-confidence" and is the core to ensure good order of blockchain network.
D. Contract Layer
The contract layer encapsulates all kinds of code scripts and algorithm mechanisms, which is the key to realize the blockchain programmability. The script system programmed according to the user's requirements can better overcome the shortcomings caused by the single function of bitcoin script. Smart contracts can be encoded on demand and deployed to the blockchain, which is automatically executed by the platform. The application of smart contract marks the transfer of blockchain from digital currency represented by bitcoin to social application.
E. Application Layer
Application layer is the standard interface layer for the interaction between blockchain and application system. It includes all kinds of application scenarios of blockchain. Users do not need to master the professional knowledge of blockchain. They can use all kinds of applications defined by the application layer by calling the standard interface provided by the application layer.
IV. THE APPLICATIONS OF BLOCKCHAIN
"Blockchain" is a general term of technology combination. It is an information technology term that comes from the combination of mathematics, cryptography, Internet communication, distributed storage, consensus protocol, and other theories and technologies. It supports the shared storage and common authentication of digital information, and can reach a common resolution through multi-party voting in the fields of justice, trade, finance, etc., to realize cooperation among multiple subjects, collaborative trust, and concerted action.
The unique security mechanism of blockchain guarantees the security of various fields; distributed public account books provide decentralized access control and management mode for data storage in various fields; encryption algorithms can improve the privacy protection for users in various fields; the formulation of intelligent contracts can customize the appropriate working mode for workflows in various fields.
(1) Application of Main Technology Platform of Blockchain (Application of Blockchain in Finance)
The cryptocurrency represented by Bitcoin has serious speculative problems. In a short period of time, such as a month or even a day, the price of Bitcoin against legal currency fluctuates by 10% or even 20%. Therefore, Bitcoin is not destined to become a payment tool that can enter public social life. Therefore, we believe that the main application scenario of Bitcoin is an investment. In the long run, the Bitcoin market is worth investing in. On one hand, from the perspective of Bitcoin development trends, the global Bitcoin trading market tends to be stable. On the other hand, government policy is expected to release positive news. After China, which was originally the third-largest country in Bitcoin transactions, closed its Bitcoin trading services, a large number of funds invested in Bitcoin flocked to Japan and South Korea, which are friendly to Bitcoin [25]. Therefore, the future development of Bitcoin is exceedingly promising.
Adding smart contracts to the blockchain is the innovation of Ethereum. The smart contract combined with the blockchain enables the content of the contract to be presented in the form of computer code, and specific operations will be automatically performed after the preset conditions are met, without relying on third-party enforcement. The potential of smart contracts is not just simply transferring funds. Many daily necessities in our lives can be connected to the Internet of Things (IoT) and used in the form of smart contracts, such as cars or door locks. At present, the development of the IoT lacks a standardized and extensible open protocol. It is already the vision of some IoT researchers that smart contracts help the birth of the IoT protocol and become part of it. Combining the open, neutral, and trustless features of Ethereum, using the open protocol of the IoT to connect devices around the world can greatly improve the operating efficiency of human society [26].
Compared with Bitcoin and Ethereum, Libra has a broader application prospect.
A. Cross-border remittance
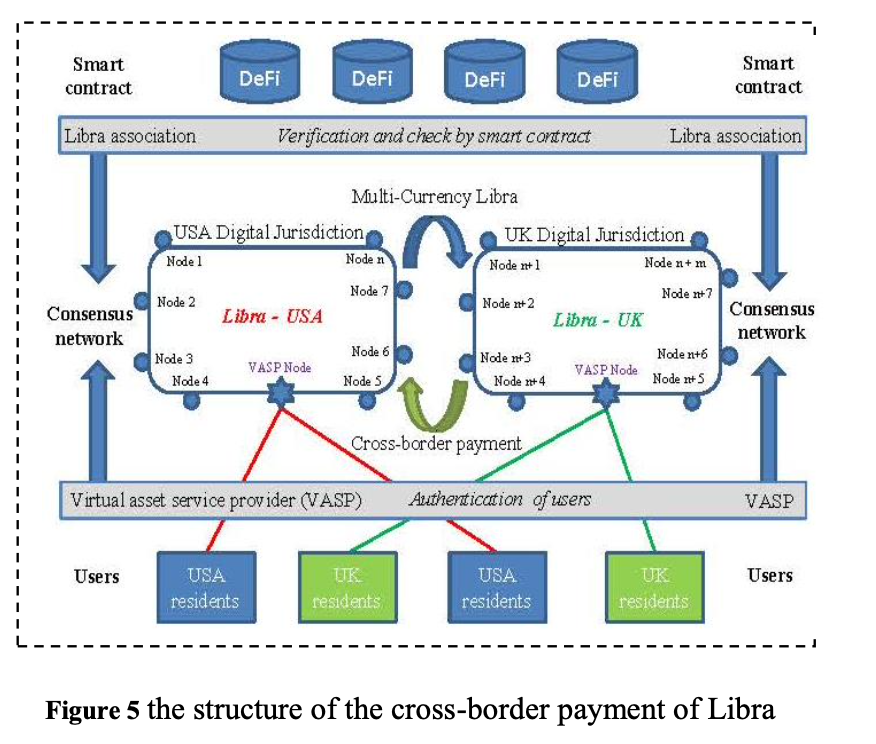
As the number of global immigrants has steadily increased year by year, the demand for cross-border transfers is also increasing. However, the traditional cross-border transfer process is inconvenient and expensive, and it cannot effectively serve areas with poor infrastructure. Libra has the characteristics of stability, low inflation, global acceptance, and interchangeability. In particular, unlike Alipay and WeChat Pay, which are linked to a single currency, Libra’s currency value is linked to a basket of currencies and does not correspond to any sovereign currency. Therefore, Libra may become essentially the most universal "currency" in the world, capable of direct exchange and settlement with the currencies of most countries in the world, avoiding the payment of high cross-border transfer fees, and being safe and efficient. Figure 5 shows the structure of the cross-border payment of Libra.
B. Domestic payment
Domestic payment may be one of the Libra's first landing scenarios. Among the first batch of institutions to join Libra, giants in consumption-related scenarios such as e-commerce, payment, travel, and music have been included. It can be expected that these scenarios will be the first to use Libra's payment mechanism in the future. In addition, Libra relies on considerable user groups and diverse application scenarios of the Facebook platform, so it will have broad development prospects in the field of digital economy payments and offline payments.
C. Economy on the blockchain
Libra's blockchain technology and smart contracts bring unlimited imagination to the economy on the blockchain. If the ecosystem and economic circulation built by Facebook can operate in a closed loop, then it can be considered that the goods and services will be priced in Libra. Libra will become the currency gauge of the economy on the blockchain. For example, financial services such as lending, wealth management, smart insurance, and crowdfunding can be born on the financial infrastructure with Libra as the universal currency.
(2) Application of blockchain technology in Internet of Things and Edge Computing
Blockchain is a kind of data structure that combines blocks in the form of a chain. Each block is connected with the previous block by hash, which realizes traceability. Blockchain technology and Internet of Things technology are decentralized and distributed, which can provide a trusted node authentication method in the process of data storage and information interaction to ensure data security. Using blockchain technology, a large number of access devices can be verified. Data protection and anti-DDoS attacks provide effective privacy protection for IoT devices. It can be divided into Perception Layer, Edge Layer, and Cloud Layer. There are three levels. Its architecture is shown in Figure 6.
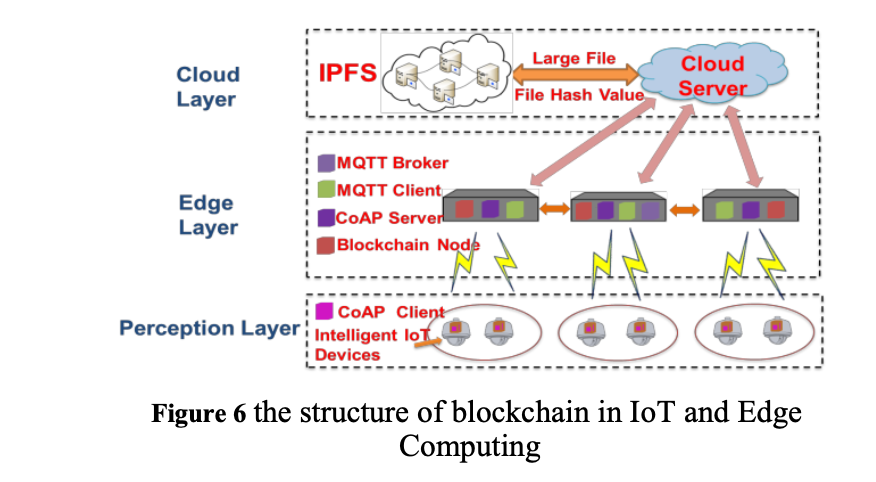
Ouamah et al. [27] proposed Fair Access, a resource access control platform for Internet of things devices. In this platform, access rights exist in the form of token. When a user visits an Internet of things device with token, the device requests the blockchain for authentication and decides whether to allow the access according to the returned result.Novo [28] proposed an IOT access control framework combining blockchain and edge computing, in which the lightweight IOT devices interact with the blockchain network through the edge management center. Each user can register as a manager, register their own managed devices in the access control blockchain, and add access control policies to the devices. PINNO et al. [29] designed the control chain, which includes four block chains, namely relationship chain, environment chain, responsibility chain and rule chain; The environment chain side records the temperature, time, network traffic and other environmental information uploaded by the Internet of things devices such as sensors; the responsibility chain records the user's request for resources and the result of the visit; the rule chain defines the access control rules based on the environment information, relationship information, responsibility information and traditional access control rules.
(3) Application of Blockchain Society Service
At present, blockchain has extended from the field of digital currency to various fields of economy and society. "Blockchain + cloud computing" [30] is a new cloud service market "blockchain as a service (baas)" that has emerged in recent years.
Blockchain as a service was first developed by Microsoft and IBM in 2015 It is proposed that through the combination of cloud computing and blockchain technology, the blockchain framework is embedded in the cloud computing platform, and the deployment and management advantages of cloud service infrastructure are utilized to provide convenient, fast, high- performance blockchain environment and supporting services for blockchain developers, support one click deployment, and support the business expansion and operation support of developers Blockchain as a service has the characteristics of one click deployment, easy to use, high security and reliability, which can effectively reduce the cost of development and use, and provide users with convenient and quick one-stop blockchain cloud service. The mainstream blockchain as a service platform is shown in Table 2.
V. CHALLENGES AND FUTURE TRENDS
In recent years, the United Nations, the International Monetary Fund and other institutions as well as a number of developed countries have released a series of reports on blockchain to explore blockchain technology and its application. at present, the application of blockchain technology has gone beyond the financial field, and gradually in the Internet of things, supply chain, credit, identity authentication, charity and other fields.
Blockchain technology originated from the open source community, and has grown in the community. Since then, it has gradually attracted the attention of financial institutions, it giants and other institutions. For example, open source projects represented by bitcoin and Ethereum mainly focus on public chain, creating a public platform for blockchain; hyperledger, launched by Linux foundation in 2015, focuses on alliance chain technology. at the same time, IBM, Microsoft azure, AWS and other Internet giants are trying their best to build the infrastructure supporting blockchain applications, blockchain as a service (BaaS).
At present, the blockchain industry is developing rapidly, and the blockchain technology has been applied more and more. However, in the field of basic research, the relevant research work at home and abroad is still in the initial stage. The technical challenges of blockchain architecture, consensus algorithm, privacy protection, smart contract and cross chain transaction are increasingly restricting the development of blockchain technology and industry. Blockchain is facing the following challenges:
A. Research on blockchain architecture
Blockchain architecture is the basis of the operation of blockchain system. However, with the increasing number of users and the scale of the system, the problems of low throughput, long transaction confirmation time, slow access speed of consensus nodes, waste of storage resources and so on become increasingly prominent, which seriously affect the use of users and industry expansion. In recent years, the industrial and academic circles have carried out some preliminary research work from the aspects of blockchain structure design.
Parallelization architecture: sharding uses the idea of parallelization to divide users into different network segments, and process disjoint transaction sets in parallel, so as to improve the overall performance. However, when dealing with transactions involving different segments, it needs to go through complex cross segment communication, which costs a lot. Plasma uses the side chain hierarchical tree to divide the whole network and "divide and conquer" to expand the transaction scale.
On chain and off chain collaborative architecture: Lightning network is based on bitcoin like blockchain. It proposes to put the transaction process under the chain as far as possible and conduct fast transaction under the chain, while on chain transaction is only used for guarantee and settlement. In essence, lightning network does not improve the performance of on chain transactions, and the off chain transactions are not stored in the blockchain, which will affect the traceability of transactions. As the "Ethereum version" of the lightning network, Raiden network can be combined with sharding and plasma to further improve the transaction processing capacity.
B. Research on High performance consensus algorithm
Blockchain consensus algorithm ensures that all nodes in the blockchain system can maintain the same transaction content and order, which is the core mechanism of the blockchain system. At present, the widely used and consensus algorithms include proof of work (POW), proof of stake (POS), Delegated proof of stake (DPOS) and Byzantine fault tolerant algorithm (PBFT) [30]. Each of these algorithms has its own advantages, but also has its own problems.
In recent years, in order to meet the needs of practical applications, some new consensus algorithms have been proposed. Algorand randomly selects a group of verifiers through the password lottery mechanism to use the optimized Byzantine protocol for consensus to improve the efficiency of consensus [31]; Bitcoin-NG proves that the selected leader publishes transaction micro block through workload, which improves the performance of pow consensus of bitcoin blockchain to a certain extent [32]; Casper consensus by confirmer of locked margin to improve the security and decentralization of POS algorithm.
However, both classic consensus algorithms such as POW and PBFT and new algorithms such as Algorand and Bitcoin- NG are faced with the problem of "Impossible Triangle" of blockchain Technology, that is, the blockchain system can only optimize two of the three goals of decentralization, high performance and security at the same time, and seeking the optimal solution of "three dilemmas" will be the main research direction and technical challenge in the future.
C. Research on smart contract of blockchain
Nick Szabo first put forward the concept of smart contract in 1996. a smart contract is a set of agreements defined in digital form, including the agreements on which the contract participants can execute these agreements. Blockchain provides a decentralized, tamper proof, open and transparent operating environment for smart contracts, so that smart contracts can be executed automatically according to the default contract protocol without trusting a third party.
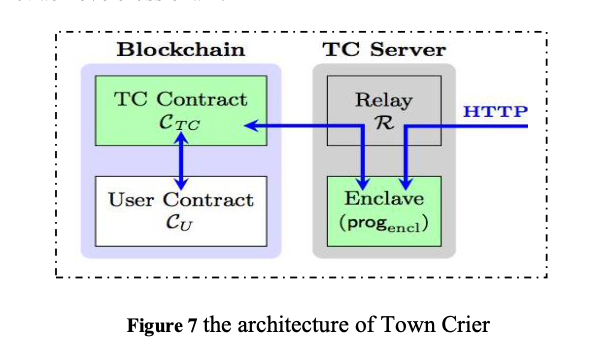
Smart contract exists in the blockchain space, and its large- scale application presupposes that it is associated with the real scene activities under the blockchain. Oraclize links smart contract with Oraclize web API through encryption proof, so that smart contract can obtain real activity data of real scene without additional trust; IC3 proposes trusted data feeding system Town Crier (TC) [33], which provides authentication, trusted and confidential data to smart contract through Intel's latest trusted hardware SGX. The basic idea of TC is to build a bridge between the smart contract system and the existing Internet system, so that the end-to-end verifiability provided by the HTTPS protocol can be extended to the smart contract system. TC solves the confidentiality problem of the blockchain: by using the confidentiality of the trusted hardware, TC can safely use the user key to access the controlled resources. It's very easy to use TC. the architecture of Town Crier shown in Figure 7.
In view of the legal problems such as the lack of authenticity, unforeseen circumstances, difficulty in accountability and lack of ex post relief, smart contracts and traditional contracts will complement each other for a long time. For the smart contract, in order to fully protect its legal effect, the smart contract will gradually deepen the understanding of laws and regulations, establish the review and transformation standards of the language of the smart contract terms, reduce the translation errors in the process of language transformation, and form a standardized contract legal audit standard. at present, smart contract is limited by the performance of the blockchain system itself. It is unable to process complex logic and high-throughput data, lack of privacy protection, and can not achieve cross chain.
D. Research on privacy protection of blockchain
With the maturity of blockchain technology and the wide use of many blockchain systems, and the future blockchain technology will play a role in more fields, the user privacy threat in blockchain system will become a more important research issue.
Monroe system uses ring signature, scope proof and Pedersen promise to realize the complete anonymity and confidentiality of the transaction, and protect the identity privacy and transaction amount of both parties in the transaction. In contrast, zerocash system uses concise non interactive zero knowledge Proofs (zk-SNARKs) and hash commitment to achieve the highest level of anonymity and transaction privacy protection for blockchain, but it still needs to pay a high computational cost when generating transaction proofs.
The privacy protection mechanism in blockchain system should not only keep the original decentralization, security and trustworthiness of blockchain system, but also protect the privacy of blockchain users from being stolen by malicious attackers, The existing implementation technology can not completely solve the threat of privacy protection or the defects of security, performance, scalability and other aspects. Combined with the existing technology, this paper puts forward the improvement direction of security, scalability and performance.
With the wide application of blockchain technology in finance, security and other fields, the privacy protection of blockchain system becomes more and more important. The attack and protection of blockchain privacy will become a research hotspot.
E. The combination of blockchain and other technologies
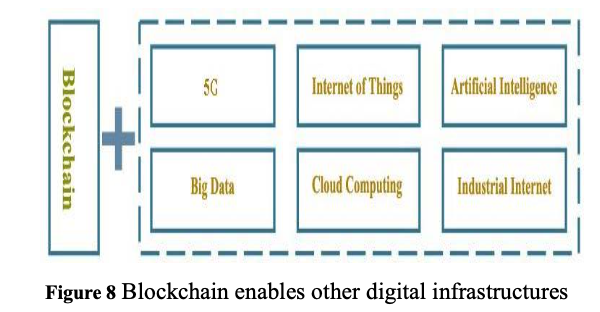
Unlike 5G, artificial intelligence, industrial Internet, Internet of things and other technologies with clear purpose and verticality, blockchain is a horizontal and connected technology. In other words, with the continuous construction and improvement of 5g, big data, artificial intelligence, industrial Internet and other digital infrastructure, there will be more new scenarios and new applications, and blockchain can play a crucial role in building trust in these new application points. Blockchain technology can play its role as a bridge to promote the interconnection, mutual benefit and mutual trust among various industries and fields, and build a new multi- level application scenario, so as to realize the interoperability development between emerging infrastructure construction industries and fields. Blockchain enables other digital infrastructures as shown in Figure 8.
F. Distributed storage based on blockchain
In the face of massive and highly concurrent data storage and computing needs in the future, distributed storage is one of the important development trends. The traditional distributed file storage still has the problem of single point of trust. The distributed storage based on blockchain has advantages in reliability, availability, cost and data privacy, such as IPFS/filecoin By migrating the workload proof incentive model of bitcoin to the scenario of providing data storage services, a new mining mechanism is designed to ensure the security of blockchain storage network.
Interstellar file system (IPFS) was proposed by Juan benet, founder of Protocol Labs. A "distributed file system" was established by connecting different devices, Content addressing method is used to split large files into data block objects to improve storage efficiency. Each file block is indexed by the hash value of the corresponding block content to establish a global Distributed Hash Table (DHT), The Merkle DAG tree data structure is used to organize the hash index of these scattered file blocks, and the index stored in the root node of the tree is used as the file addressing hash value.
Distributed storage and blockchain naturally have a certain matching, and both are based on distributed system. As an under chain storage scheme, distributed storage can expand the storage space of blockchain, which is inefficient. In addition, distributed storage can optimize the storage efficiency of the blockchain, release the storage space on the chain to store more critical information, without affecting the availability of the blockchain when processing big data.
VI. DISCUSSION AND FUTURE DIRECTIONS
In this paper, through the literature related to blockchain technology, the concept of blockchain technology, blockchain technology foundation, blockchain architecture, blockchain technology application and challenges and future trends the purpose is to help scientific researchers engaged in blockchain technology understand the current research status, research hotspots and blockchain technology The evolution trend of technology in the future.
/images/306d/d4_0.png
